Exchange 2016, 2013, and 2010 servers participating in a Database Availability Group (DAG) also use mailbox replication to prevent data loss. The active and passive node concept is the same as for Exchange 2007 CCR configurations, but DAG configurations permit two or more Exchange servers to be clustered together. In DAG configurations, an Exchange server’s active mailboxes are continuously replicated to passive mailboxes on one or more Exchange servers. DAG configurations allow a single Exchange server to host the entire set of active mailboxes and all other Exchange servers in the DAG host a copy of the passive mailboxes. Or, each server in the DAG can host active and passive mailboxes simultaneously. As an example, assume a DAG has three Exchange server members:
| • | Exchange_North |
| • | Exchange_South |
| • | Exchange_East |
The DAG also has the following Exchange databases in operation:
| • | DB_North |
| • | DB_South |
| • | DB_East |
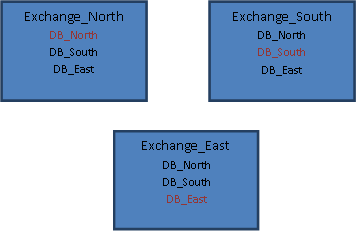
An example of how the databases may be protected by the DAG is shown below. The database names shown in red are the active copies. All others are the passive copies that are the replication targets. Each database is active on one Exchange server and replicated to all other Exchange servers.

Microsoft recommends backing up the passive copies of databases to reduce the workload on the server hosting the active copies. One way to facilitate this backup strategy is to host all active copies on a single server and replicate them to one or more DAG members, as shown in the figure below. All active databases are located on the server Exchange_North, while Exchange_South and Exchange_East host multiple passive copies. The Unitrends agent is then used to backup the databases on Exchange_South and Exchange_East at regular intervals.

Exchange 2016, 2013, 2010, and 2007 provide two VSS writers that are used for backup. The Exchange Info Store writer manages the backup of active databases. The Exchange Replication writer manages the backup of passive (or replicated) databases. The Unitrends agent can backup using either writer. When a database backup starts, the agent determines if it is the active or passive copy, then uses the appropriate Exchange writer for the operation. In replicated configurations, you can schedule backups of all databases on any of the servers. A database failover condition won’t affect the next backup since the agent will backup databases in either state.