Recovering files from virtual machine backups
You can recover files from host-level backups and host-level backup copies of Windows and Linux VMs. File recovery is supported for VMs that reside on VMware, Hyper-V, AHV, and XenServer hosts. A single file-level recovery can be performed on multiple VMs simultaneously.
Recovery procedures can be run from the backup appliance or from the backup copy target appliance:
| • | Any host-level backup of a Windows or Linux VM – Recovering from a local backup or imported backup copy involves creating a recovery object on the backup appliance that contains files from the backup. You recover files by downloading directly from this object or by mounting the object to a recovery target machine. |
| • | Any host-level backup of a Windows or Linux VM – Recovering directly from a backup copy that resides on a target appliance or resides in the Unitrends Cloud involves creating a recovery object on the target appliance or in the Unitrends Cloud. You recover files by downloading directly from this object or by mounting the object to a recovery target machine. |
| • | Indexed VMware host-level backup of a Windows VM – Run the recovery on the local backup appliance to search a VMware virtual machine's indexed backups for files that meet specified criteria and recover selected items to an agent-based Windows asset. |
The method you use to recover files is determined by the following:
| • | Where you run the procedure. Procedures run on a backup appliance differ from those run on a backup copy target appliance. |
| • | Whether you are recovering from a backup, imported backup copy, or hot backup copy. |
| • | The operating system (OS) and configuration of the protected VM. |
| • | Whether you are running indexed host-level backups of a VMware Windows virtual machine. |
If file recovery is not supported for your Windows or Linux VM, recover the virtual machine instead as described in Recovering a virtual machine.
Use the Recovering from an indexed VMware backup of a Windows VM by using Search Files, Windows file-level recovery, or Linux file-level recovery procedures to recover files. The recovery procedure you use is determined by the following: whether the backup is an indexed VMware backup, where you are running the procedure and whether you are recovering from a local backup, from an imported backup copy, or directly from a hot backup copy. See the following table for a description of the options you can use in each case:
|
Backup type and location |
Run from |
Use this procedure to create the recovery object |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Host-level backup on the local appliance |
Backup appliance |
Run the Windows file-level recovery or Linux file-level recovery procedure from the backup appliance to recover files from a local backup or from an imported backup copy.
To import a backup copy, see To import a cold backup copy or To import a hot backup copy. |
||||||
|
Indexed backup of a VMware Windows VM on the local appliance |
Backup appliance |
Run the Recovering from an indexed VMware backup of a Windows VM by using Search Files procedure from the backup appliance to search indexed backups. Note: This recovery procedure searches indexed local backups only. Search Files cannot be used to search imported backup copies. |
||||||
|
Host-level backup copy in the Unitrends Cloud or on a backup copy target appliance (release 9.1 or later only) |
Source backup appliance |
Run the Windows file-level recovery or Linux file-level recovery procedure from the source backup appliance to recover files directly from a backup copy that resides on a target appliance or resides in the Unitrends Cloud. Both the source appliance and the target appliance must be running release 9.1 or later.
|
||||||
|
Host-level backup copy on a backup copy target appliance |
Backup copy target appliance |
Run the Windows file-level recovery or Linux file-level recovery procedure from the backup copy target appliance to recover files from a hot backup copy that resides on that target appliance.
|
Use this procedure to search a VMware Windows VM's indexed backups for files/folders that meet specified criteria and recover selected items from the search results.
Notes:
| • | The backup appliance must be running release 10.5 or higher to run this procedure. |
| • | This procedure can only be used for local backups that were run with the Edit Asset > Index Backups option. For details on configuring this option, see To edit a virtual machine asset. |
| • | During the procedure, you will select an agent-based Windows asset where files will be recovered. Choose from the Windows assets that have been added to the appliance. To recover files to the original location or to another VM, install the Unitrends agent on the Windows VM (see Installing the Windows agent), then add the VM to the backup appliance as an agent-based asset (see To add an agent-based asset). |
| • | File search of imported backup copies is not supported. Recover by browsing the imported backup instead (see Windows file-level recovery or Linux file-level recovery). |
| • | File search is not supported for recovery of ReFS filesystems. Recover by browsing the backup instead (see Windows file-level recovery ). |
| 1 | Log in to the backup appliance. |
| 2 | Click Recover > Backup Catalog > Search Files. |
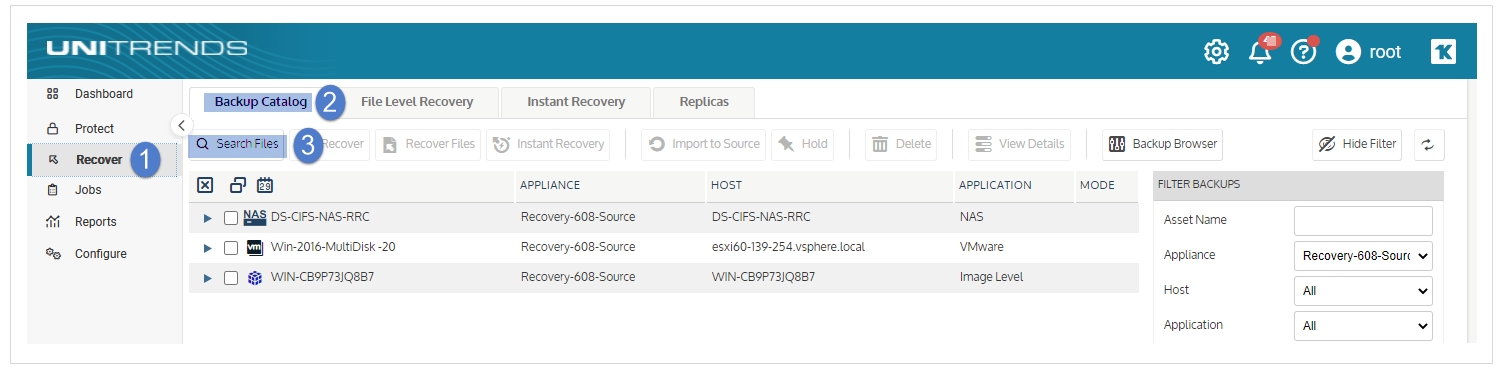
| 3 | In the Type list, select Backup. |
| 4 | Select the VMware Asset whose backups will be searched. VMware assets are listed as VM_name (host_name). |
| 5 | Enter one or more search options: |
|
Search Options |
Description |
|---|---|
|
String |
Enter text to search. The wildcard character * is supported. |
|
Match Case |
Select to match the letter case of the entered string. |
|
From/To |
Use to search for files that were last modified within the specified date range. Results do not include files modified on the From or To date. |
|
Size |
Use to search for files that meet this size criteria. |
|
Advanced |
Click to search using a regular expression. |
| 6 | Click Search. |
All indexed backups of this VM stored on the appliance are searched for matching files.

| 7 | In the results list, click to select files/folders to recover. |
Notes:
| • | All items you select must be from a single backup. Check the Backup ID to determine an item's backup. If you select items from multiple backups, the Next button becomes disabled. |
| • | Softlinks cannot be downloaded and are not included in the search results. |
| 8 | Click Next. |

| 9 | Select the Windows Asset where the files will be recovered. |
The list contains agent-based assets that have been added to the appliance. To add a target asset, install the Unitrends agent on the asset (see Installing the Windows agent), then add the asset (see To add an agent-based asset).
| 10 | (Optional) Enter a Directory path or click Browse and select a Directory path from the drop-down list. |
| • | If the directory does not exist, the job creates it on the target asset. |
| • | Leave the Directory field empty to recover files to their original location. |
| 11 | (Optional) Specify Exclusions. |
| 12 | (Optional) Specify Advanced Options. |
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Commands to run pre-restore |
To run a command or script on the asset before the recovery, enter the full path to the command or script in the Commands to run pre-restore field. For example, C:\Data\script.bat or /usr/jsmith/script.sh. |
|
Commands to run post-restore |
To run a command or script on the asset after the recovery, enter the full path to the command or script in the Commands to run post-restore field. For example, C:\Data\script.bat or /usr/jsmith/script.sh. |
|
Preserve directory structure |
Check this box to preserve the existing file structure within the target directory. Note: To recover the file(s) to the original location, Preserve Directory Structure must be selected. If you attempt to recover to the original location and uncheck this box, the recovery fails. |
|
Overwrite existing files |
If this box is checked, files in the Target Directory may be overwritten. (See Overwrite existing files and Restore newer files only options for details.) This is useful if you are recovering an updated version of a document and only want the most up to date version. |
|
Restore newer files only |
Check this box to recover a file only if its date is newer than the existing version in the Target Directory. (See Overwrite existing files and Restore newer files only options for details.) If the file does not exist in the Target Directory, the file is recovered. |
|
Set file dates to today |
Check this box to update the recovered files with the recover date and time. If not checked, file dates are not updated during the recovery. |
|
UNIX text conversion |
When recovering UNIX Text files to MS-DOS systems, checking this option prevents new lines from being converted to CR-LF. |
This table describes how Overwrite existing files and Restore newer files only work if the file exists in the Target Directory.
|
Option selected? |
Recovery behavior |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Windows backup |
Non-Windows backup |
|||||||
|
Overwrite existing files = Yes |
Recovers the file and overwrites the existing file. |
|
||||||
|
Overwrite existing files = Yes |
Recovers the file and overwrites the existing file. |
Recovers the file and overwrites the existing file. |
||||||
|
Overwrite existing files = No |
Does not recover the file. |
Does not recover the file. |
||||||
| 13 | Click Save. |
| 14 | Click OK to close the Notice message. |

| 15 | To monitor the recovery job: |
| • | Select Jobs > Active Jobs. |
| • | Select the job in the list and click View Details. |

| • | The recovery is complete when the job's status changes to Success. |

| 16 | Access the recovered files on the recovery target. |
Note: Files that are locked because they are in use in the location where you are performing the restore (system files, database files, etc.) cannot be restored while the system is live. During recovery, these files are moved to a temporary location and an entry is added into the registry telling Windows to restore the files to their actual final location on the next boot.
Use the following procedures to recover files from a backup, imported backup copy, or hot backup copy of a Windows VM.
Notes:
| • | Hyper-V – Recovery of selected files or pathnames that contain non-UTF-8 compatible characters is not supported. |
| • | VMware – Do not use these procedures to recover files from an indexed VMware backup. Instead, see Recovering from an indexed VMware backup of a Windows VM by using Search Files. |
The following requirements and considerations apply to recovering files from a host-level backup or host-level backup copy of a Windows VM by creating a recovery object:
|
Prerequisite or consideration |
Description |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Supported recovery methods |
To recover files from a host-level backup or copy, the appliance creates a recovery object that contains the backup's files. For some Windows VMs, this object is also exposed as a CIFS (Samba) share and/or an iSCSI LUN on the backup appliance. After you create the recovery object, you will view it on the File Level Recovery tab to see whether the CIFS and iSCSI options are available. You can recover files from this object in several ways. Options include:
|
||||||||||||
|
Recovery target requirements |
The target can be configured with basic, GUID Partition Table (GPT), or dynamic disks. All configured disks must have unique names. To use a CIFS share for the recovery, the target Windows asset must be able to access the appliance's Samba share:
Note: Upgrading from a pre-10.4.8 version does not change the SMB 1.0 setting. (To configure your appliance to use SMB 2.0, see How Unitrends supports SMBv2.) |
||||||||||||
|
You must recover by mounting the iSCSI LUN to perform the following tasks:
Note: ReFS limitation - ReFS file system versions are not compatible with all Windows operating system versions. To avoid compatibility issues, recover ReFS files by mounting the iSCSI LUN on a machine whose operating system version is the same or later than that of the machine where the backup was taken.
Note: For the recovery, iSCSI disks are writable and a 1 GB write limit is enforced. Errors display on the recovery target machine if more than 1 GB is required. In this case, you cannot recover by using iSCSI. Recover files by downloading to a .zip file or by mounting the CIFS share, or perform a VM recovery. |
Use one of these procedures to create the recovery object:
Note: If a previously-created recovery object is still mounted for the VM, you must remove it before creating a new one.
Run this procedure on the backup appliance to recover from a backup or imported backup copy.
| 1 | Log in to the backup appliance. |
| 2 | Select Recover and click the Backup Catalog tab. |
(Optional) Use Filter Backups to the right to customize the backups that display. For details, see Working with custom filters.
| 3 | Expand the asset and select the backup or imported backup copy from which you want to recover files. |
(To import a backup copy, see To import a cold backup copy or To import a hot backup copy.)
| 4 | Click Recover Files. |

| 5 | Click Confirm to continue. The appliance creates the recovery object. |
Note: If you receive an error on a Unitrends Backup appliance while creating the recovery object, increase the memory allocation for the Unitrends Backup VM by using the host that manages it.
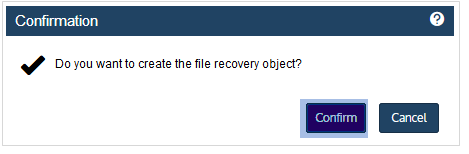
| 6 | Click View FLR. |
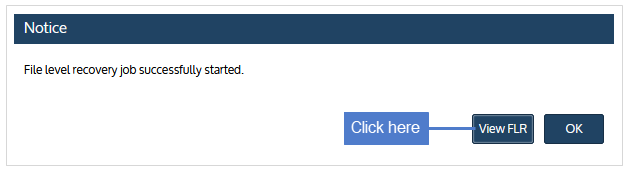
Proceed to " Step 3: Recover files".
Run this procedure on the backup appliance to recover from a backup copy that resides on a target appliance or in the Unitrends Cloud.
| 1 | Log in to the source backup appliance. |
| 2 | Select Recover and click the Backup Catalog tab. |
| 3 | Use Filter Backups to the right to display hot backup copies: |
| • | In the Type box, select Backup Copy (Hot). |
| • | (Optional) Select other filter options. For details, see Working with custom filters. |
| • | Click Filter. |
| 4 | Expand the asset and select the hot backup copy from which you want to recover files. |
| 5 | Click Recover Files. |

| 6 | Click Confirm to continue. The appliance creates the recovery object in the Cloud or on the target appliance. |
Notes:
| • | If your appliance is a Unitrends Backup virtual appliance and you receive an error while creating the recovery object, increase the memory allocation for the Unitrends Backup VM using the host that manages it. |
| • | Recovery objects created in the Unitrends Cloud are automatically removed after 96 hours. |

| 7 | Click View FLR to view the recovery object on the File Level Recovery tab. The recovery object Name is AssetName (on the target). |


Proceed to " Step 3: Recover files".
Run this procedure on the target appliance to recover from a backup copy that resides on that target appliance.
| 1 | Log in to the backup copy target appliance. |
| 2 | Select Recover and click the Backup Catalog tab. |
| 3 | Use Filter Backups to the right to display hot backup copies: |
| • | In the Type box, select Backup Copy (Hot). |
| • | (Optional) Select other filter options. For details, see Working with custom filters. |
| • | Click Filter. |
| 4 | Expand the asset and select the hot backup copy from which you want to recover files. |
| 5 | Click Recover Files. |

| 6 | Click Confirm to continue. The appliance creates the recovery object on the target appliance. |
Note: If your appliance is a Unitrends Backup virtual appliance and you receive an error while creating the recovery object, increase the memory allocation for the Unitrends Backup VM using the host that manages it.

| 7 | Click View FLR to view the recovery object on the File Level Recovery tab. |


| 8 | Proceed to " Step 3: Recover files". |
View the recovery object on the File Level Recovery tab to see which recovery options are supported for the VM you selected. Use one of the following procedures to recover files. For a description of each method, see Recovery procedures overview.
| 1 | On the File Level Recovery tab, locate the recovery object. |
Recovery objects display on the tab with the following details: the name of the VM asset for which the object was created, the status of the object, the date and time it was created, the length of time it has existed on the appliance, and whether it can be accessed through iSCSI or CIFS.
| 2 | Select the recovery object and click Browse/Download. |

| 3 | In the File Browser, select or drag files and/or directories to recover. |
Note: Softlinks (also called symbolic links) are excluded from download. If you select a directory that contains files and softlinks, only the files are downloaded.
| 4 | Click Download. |

| 5 | Click Confirm to download the selected files to a .zip file. The .zip file is downloaded to your browser's default location. |
Notes:
| • | Volumes are assigned numbers during recovery that do not necessarily match the numbers from the original disk. |
| • | The duration of the download is impacted by various factors, such as the size of the files, bandwidth, and download speed. |
| • | Persistent browser and UI sessions are required to create the .zip file in the browser's default download location. If you close the browser or UI session during the recovery, you must run a new job. |
| 6 | When the download completes, the Unitrends-Restore.zip file displays in the browser. Select whether to open or save the file. |
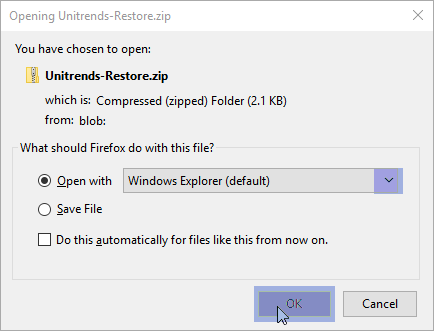
| 7 | Access the recovered files in the download location and move them to another location on the local machine. |
Note: The Windows file explorer contains a setting to hide protected/system files. Turn off this setting to access all files.
Proceed to Step 4: Remove the recovery object from the appliance.
| 1 | Select Recover and click the File Level Recovery tab. |
Recovery objects display with the following details: the name of the VM asset for which the object was created, the status of the object, the date and time it was created, the length of time it has existed on the appliance, and whether it can be accessed through iSCSI or CIFS.
| 2 | Select the recovery object and click Show Details. |

| 3 | Note the CIFS path that displays in the File Level Recovery Details window. You will need this path to mount the CIFS share on the target machine. |

| 4 | Log in to the recovery target workstation. |
| 5 | Enter the CIFS path into a file browser on the recovery target. |

| 6 | Browse the share to locate the files you want to recover. |
Notes:
| • | Volumes are assigned numbers during recovery that do not necessarily match the letters from the original disks. |
| • | The Windows file explorer contains a setting to hide protected/system files. Turn off this setting to access all files. |

| 7 | Move selected files to another location on the local machine. |
| 8 | Disconnect the network share by right-clicking the share and selecting Disconnect. |
| 9 | Proceed to Step 4: Remove the recovery object from the appliance. |
| 1 | Log in to the recovery target workstation. |
| 2 | Launch the iSCSI Initiator from Administrative Tools in the Control Panel. |

| 3 | In the Target field, enter the appliance IP address and click Quick Connect.... |
The Discovered targets field populates with a list of iSCSI LUN targets.
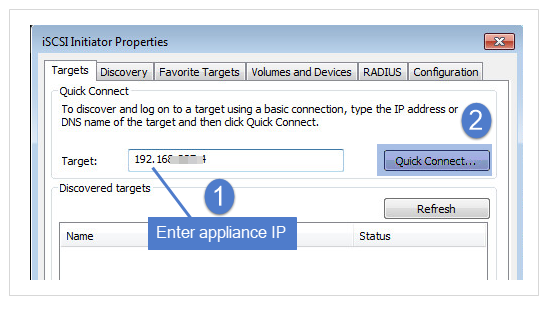
| 4 | Select the iSCSI target from the list. |
| 5 | The iSCSI target is discovered and connected to the local machine. Click Done. |

| 6 | Use Disk Manager or diskpart to verify that the mounted iSCSI disk is online. If not, bring the drive online. |
| 7 | Return to the iSCSI Initiator. On the Volumes and Devices tab, click Auto Configure to map drives from the iSCSI target to the local machine (or map them manually if you prefer). |
Note: Volumes are assigned letters during recovery that do not necessarily match the letters from the original disks.

| 8 | Access the files under the mapped drives and move them to another location on the local machine. |
Note: The Windows file explorer contains a setting to hide protected/system files. Turn off this setting to access all files.

| 9 | Use the iSCSI Initiator to disconnect from the LUN. |


| 10 | Proceed to Step 4: Remove the recovery object from the appliance. |
To ensure optimal performance, remove the recovery object from the appliance.
Warning! If you mounted the CIFS share or iSCSI LUN, be sure to unmount it from the target before you remove the recovery object. Removing the recovery object while the target is still connected causes undesired results and errors on the target machine.
To remove a file-level recovery object
| 1 | Select Recover and click the File Level Recovery tab. |
| 2 | Select the recovery object. |
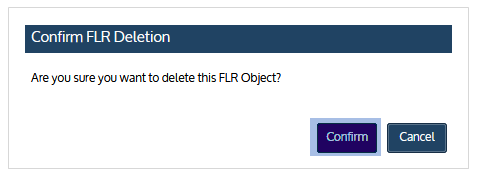
| 3 | Click Remove. |

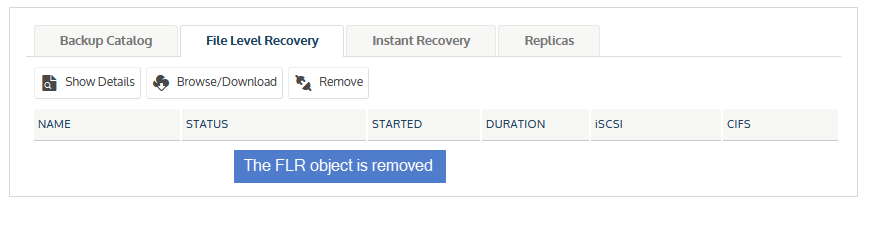
| 4 | Click Confirm to continue. The object is removed and no longer displays on the File Level Recovery tab. |
Use the following procedures to recover files from a backup, imported backup copy, or hot backup copy of a Linux VM.
The following requirements and considerations apply to recovering files from a host-level backup or host-level backup copy of a Linux VM by creating a recovery object:
|
Prerequisite or consideration |
Description |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Supported recovery methods |
To recover files from a host-level backup or copy, the appliance creates a recovery object that contains the backup's files. For some Linux VMs, this object is also exposed as a CIFS (Samba) share and/or an iSCSI LUN on the backup appliance. After you create the recovery object, you will view it on the File Level Recovery tab to see whether the CIFS and iSCSI options are available. You can recover files from this object in several ways. Options include:
|
|||||||||
|
Linux kernel version |
The Linux VM cannot be running a higher Linux kernel version than the Unitrends appliance. If your Linux VM is running a higher Linux kernel version, recover the virtual machine instead as described in Recovering a virtual machine. |
|||||||||
|
Configuration of the protected Linux VM |
These requirements apply to the original Linux VM whose backup or backup copy will be used for the recovery:
|
|||||||||
|
To recover by mounting the iSCSI LUN, the following prerequisites and considerations apply:
|
Use one of these procedures to create the recovery object:
Note: If a previously-created recovery object is still mounted for the VM, you must remove it before creating a new one.
Run this procedure on the backup appliance to recover from a backup or imported backup copy.
| 1 | Log in to the backup appliance. |
| 2 | Select Recover and click the Backup Catalog tab. |
(Optional) Use Filter Backups to the right to customize the backups that display. For details, see Working with custom filters.
| 3 | Expand the asset and select the backup or imported backup copy from which you want to recover files. |
(To import a backup copy, see To import a cold backup copy or To import a hot backup copy.)
| 4 | Click Recover Files. |

| 5 | Click Confirm to continue. The appliance creates the recovery object. |
Note: If you receive an error on a Unitrends Backup appliance while creating the recovery object, increase the memory allocation for the Unitrends Backup VM by using the host that manages it.

| 6 | Click View FLR. |

Proceed to Step 3: Recover files.
Run this procedure on the backup appliance to recover from a backup copy that resides in the Unitrends Cloud or resides on the target appliance.
| 1 | Log in to the source backup appliance. |
| 2 | Select Recover and click the Backup Catalog tab. |
| 3 | Use Filter Backups to the right to display hot backup copies: |
| • | In the Type box, select Backup Copy (Hot). |
| • | (Optional) Select other filter options. For details, see Working with custom filters. |
| • | Click Filter. |
| 4 | Expand the asset and select the hot backup copy from which you want to recover files. |
| 5 | Click Recover Files. |

| 6 | Click Confirm to continue. The appliance creates the recovery object in the Cloud or on the target appliance. |
Notes:
| • | If your appliance is a Unitrends Backup virtual appliance and you receive an error while creating the recovery object, increase the memory allocation for the Unitrends Backup VM using the host that manages it. |
| • | Recovery objects created in the Unitrends Cloud are automatically removed after 96 hours. |

| 7 | Click View FLR to view the recovery object on the File Level Recovery tab. The recovery object Name is AssetName (on the target). |


| 8 | Proceed to Step 3: Recover files. |
Run this procedure on the target appliance to recover from a backup copy that resides on that target appliance.
| 1 | Log in to the backup copy target appliance. |
| 2 | Select Recover and click the Backup Catalog tab. |
| 3 | Use Filter Backups to the right to display hot backup copies: |
| • | In the Type box, select Backup Copy (Hot). |
| • | (Optional) Select other filter options. For details, see Working with custom filters. |
| • | Click Filter. |
| 4 | Expand the asset and select the hot backup copy from which you want to recover files. |
| 5 | Click Recover Files. |

| 6 | Click Confirm to continue. The appliance creates the recovery object on the target appliance. |
Note: If your appliance is a Unitrends Backup virtual appliance and you receive an error while creating the recovery object, increase the memory allocation for the Unitrends Backup VM using the host that manages it.

| 7 | Click View FLR to view the recovery object on the File Level Recovery tab. |


Proceed to Step 3: Recover files.
Use one of the following procedures to recover files. For a description of each method, see Recovery procedures overview.
| 1 | On the File Level Recovery tab, locate the recovery object. |
Recovery objects display on the tab with the following details: the name of the VM asset for which the object was created, the status of the object, the date and time it was created, the length of time it has existed on the appliance, and whether it can be accessed through iSCSI or CIFS.
| 2 | Select the recovery object and click Browse/Download. |

| 3 | In the File Browser, select or drag files and/or directories to recover. |
Note: Softlinks (also called symbolic links) are excluded from download. If you select a directory that contains files and softlinks, only the files are downloaded.
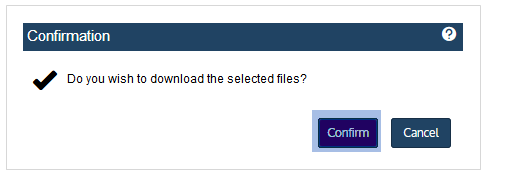
| 4 | Click Download. |

| 5 | Click Confirm to download the selected files to a .zip file. The .zip file is downloaded to your browser's default location. |
Notes:
| • | Volumes are assigned numbers during recovery that do not necessarily match the numbers from the original disk. |
| • | The duration of the download is impacted by various factors, such as the size of the files, bandwidth, and download speed. |
| • | Persistent browser and UI sessions are required to create the .zip file in the browser's default download location. If you close the browser or UI session during the recovery, you must run a new job. |
| 6 | When the download completes, the Unitrends-Restore.zip file displays in the browser. Select whether to open or save the file. |

| 7 | Access the recovered files in the download location and move them to another location on the local machine. |
Note: The Windows file explorer contains a setting to hide protected/system files. Turn off this setting to access all files.
| 8 | Proceed to Step 4: Remove the recovery object from the appliance. |
| 1 | Select Recover and click the File Level Recovery tab. |
Recovery objects display with the following details: the name of the VM asset for which the object was created, the status of the object, the date and time it was created, the length of time it has existed on the appliance, and whether it can be accessed through iSCSI or CIFS.
| 2 | Select the recovery object and click Show Details. |

| 3 | Note the CIFS path that displays in the File Level Recovery Details window. You will need this path to mount the CIFS share on the target machine. |

| 4 | Log in to the recovery target workstation. |
| 5 | Enter the CIFS path into a file browser on the recovery target. |

| 6 | Browse the share to locate the files you want to recover. |
Note: Volumes are assigned numbers during recovery that do not necessarily match the numbers from the original disks.

| 7 | Move selected files to another location on the local machine. |
| 8 | Disconnect the network share by right-clicking the share and selecting Disconnect. |
| 9 | Proceed to Step 4: Remove the recovery object from the appliance. |
Use these steps to mount the iSCSI LUN to the target machine and copy the files.
| 1 | In the appliance UI, select Recover and click the File Level Recovery tab. |
Recovery objects display with the following details: the name of the VM asset for which the object was created, the status of the object, the date and time it was created, the length of time it has existed on the appliance, and whether it can be accessed through iSCSI or CIFS.
| 2 | Select the recovery object and click Show Details. |

| 3 | Note the full path of the iSCSI mount point directory that displays in the File Level Recovery Details window. You will need this path to mount the iSCSI object on the target machine. The mount point is normally: /iscsi_flr. |

| 4 | Log in to the recovery target. |
| 5 | Enter the following command to change to the /tmp directory: |
# cd /tmp
| 6 | Run the following command to copy the iscsi_flr script from the backup appliance: |
# wget http://<appliance IP>/iscsi_flr
| 7 | After the script downloads, add the execute permission: |
# chmod +x iscsi_flr
| 8 | Run the following command to mount the recovery object: |
# ./iscsi_flr mount
| 9 | Enter the appliance IP address: |
# Enter address of the Unitrends backup system: <appliance IP>
| 10 | Enter the full path of the mount point directory. The full path is likely: /iscsi_flr. This procedure uses /iscsi_flr as an example. Be sure to enter the actual mount point that was displayed in the appliance UI. |
# Enter mount point directory (full path): /iscsi_flr
| 11 | Discovered iSCSI targets display. Choose the target that contains the appliance IP by entering its number. In this example, session 1 is the appliance target: |

# Choose a session to restore from: <sessionNumber>
| 12 | Verify that the mounted iSCSI disk is online. If not, bring the drive online. |
| 13 | Change to the mount point directory to access the files. For example: |
# cd /iscsi_flr
| 14 | Move selected files to another location on the local machine. |
| 15 | Run the following command from the /tmp directory to disconnect from the LUN: |
# ./iscsi_flr unmount
| 16 | Proceed to Step 4: Remove the recovery object from the appliance. |
To ensure optimal performance, remove the recovery object from the appliance.
Warning! If you recovered by mounting a LUN, be sure to unmount the LUN from the target before you remove the recovery object. Removing the recovery object while the target is still connected causes undesired results and errors on the target machine.
To remove a file-level recovery object
| 1 | Select Recover and click the File Level Recovery tab. |
| 2 | Select the object to remove from the appliance. |
| 3 | Click Remove. |

| 4 | Click Confirm to continue. The object is removed and no longer displays on the File Level Recovery tab. |

